
You’re here right now using the Internet to read this lecture and learn new skills, which means you’ve decided to become a successful online worker, right?
The fact that you are about to become an online employee originates from the fact that the Internet is used as a business environment.
Senator Ron Wyden once said:
Therefore, it is important that you learn about this amazing business setting since it is about to become your working environment. You would explore your brick-and-mortar company and its marketplace when starting to work for them, wouldn’t you?
So, we can agree that pursuing an online career is inconceivable without having a clue about how the Internet actually works.
Just like you simply CANNOT imagine someone being a professional chef in a top-class well-known international restaurant but being clueless about how to handle various tools in the kitchen (knives, pots, cookers) or how to process, mix and match different ingredients to prepare a truly delicious meal.
In other words, you do NOT want to be ignorant!
On the contrary, you are ready to dig deeper into the secrets of this magnificent tool and set your feet firmly on the path to a successful online career.
That’s why we’re going to give you a brief but exquisite insight into the following in this lesson:
- The history of the Internet
- The difference between URLs and domains
- The importance and differences between HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP
- How data move around the Internet
- What packets of information are
- What archive.org is, as well as
- How and why you can find these basic concepts beneficial in your line of work
Eager to find out? Let’s get down to it?
Short History of the Internet
It’s well-known that the Internet is considered to be one of the greatest inventions of all times.
Nowadays, it is impossible to imagine our lives without it. Just try to think about it for a moment – What can you do online today and what were you able to do just several years ago?
The growth and development of the Internet are incredible, aren’t they? But literary, almost everything you can think of now can be done on the Internet.
It’s late in the evening, you are sitting in your comfortable home, and you feel like reading? – There are many e-libraries and many e-books you can download or read online.
Do you want to educate yourself, to go to university, switch careers? – No problem, there are many of those who provide online courses.
Do you want to get in touch with your friend who lives on the other side of the planet? – Wow, there are many FREE ways to do that now.
And, of course – Do you want to work from the comfort of your home or run an online business? – Well, you already know the answer to this.
Do you see where this is going? Everything you want to know or find out is now just a few clicks away.
But have you ever wondered how and when the magic story about the Internet began?
Many great articles have been written on that topic, such as History of the Internet and this one about the Internet changes over the past 20 years.
Or, if you are more of a visual type, here is a great video about the history of the Internet.
Follow the links for more detailed information. You will find out how and why the Internet got started, what were those very first experiments when people emailed each other on the network and created hyperlinks, as well as what amazing changes it has gone through just in the last decades or even a couple of years.
All the information on the Internet was text-based mainly in the very beginning. Can you imagine how it must have looked?
Now, try to imagine the appearance of an online store at that time. Let’s take a peek at a couple of those very early Internet pages, shall we?
Here’s what the old eBay web page looked like way back in 1999. Follow the link to see its layout today.

And here’s the look of the ancient Pizza Hut website. They were among if not the first to enable buying via the Internet.
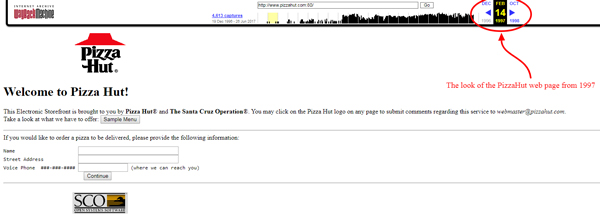
Not especially impressive, right?
Here’s what their website looks like now.

Isn’t there a huge difference between these old and up-to-date versions of the websites?
You can have more fun checking out how 20 popular websites looked in the early days of their existence as well as find out about 23 ancient websites that are still alive.
Being given the background, don’t you appreciate this marvellous tool a lot more now? We bet you do.
So, let’s get to know how it works and dive a bit deeper into its secrets so that you can understand and use it to its maximum!
Web Address and Its Elements
You’ve seen how fast the Internet is developing and how radically it’s changing. You’ve also realised how important for you as an online worker it is to keep your finger on its pulse, right?
Nice! Now, let’s see why it’s also super important for you to understand the basic networking terminology being discussed in this lesson such as URLs, domains, HTTP, HTTPS, packets of information, etc. and the nuances of their meanings.
Primarily because you will NOT work alone but with a whole online team, which means you’ll have to communicate effectively with your co-workers from all over the world on a daily basis.
How could you possibly do that if you don’t share the same language? Yes, you speak English well, but here we’re talking about the lingo of the trade. Said differently, we have on mind those expressions peculiar to each industry.
In order to become an appreciated member of an online team, you MUST be able to use the right specialised language when collaborating with your colleagues.
Then, let’s talk about those specific terms, their meanings, use and importance!
A basic notion you have to understand in this context is the meaning of address. When you think about an address, you, naturally, think about a location. The more precise the address is, the better. For example:
Imagine someone asks you where you live and you reply: ‘I live East from here.’
How does that sound to you? Wouldn’t a proper answer be more like: ‘I live at 12 Smith Street.’
Because, when you say this, everyone understands your exact physical address, right? It’s specific and unique.
The same goes for the locations of websites and online stores on the Internet.
You can find your physical address written down in your passport, ID or driver’s license. But, when it comes to Internet websites, eCommerce stores included, the address is written in the address bar of your browser.
Take a look at the part of the eCommerce store Simplicity Sofas, seen in a Google Chrome browser:
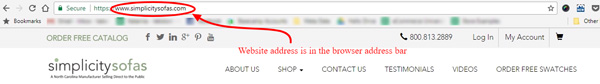
This looks much different than a street name and the number, doesn’t it? It has different elements, so let’s name them and explain what they mean.
This entire string of characters is an URL. It consists of, at least, a protocol and domain. Domain then can be broken down to a subdomain, root domain and a domain suffix. There can be more elements than this, but these are the basic ones.
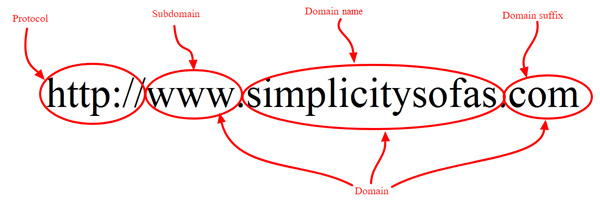
- A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is this entire address. It tells which protocol needs to be used to locate the resource on the web and in which domain to look for those resources. In simpler words, it refers to a website or Internet address
- On the other hand, a domain is the location of the website. It points your web browser to the exact place on the Internet from where it should download the web page and present it to you.
A domain name can consist of 63 characters maximum or 1 character minimum. An example of a domain name could be: www.simplicitysofas.com
If you know that protocol + www (in this example) + root domain gives a URL. This leaves us with the fact that simplicitysofas.com
Is the root domain, consisting of the domain name and the domain suffix (more about it below.)
- So, what is ‘www’ then? – That is a subdomain. It is used to distinguish the content, and in many cases, it can be left out. It doesn’t have to be ‘www’, but also could be ‘ftp’ or ‘support’, etc.
- The last piece of a domain name is known as a domain suffix or TLD (Top Level Domain). It identifies the type or location of the website.
There are many different domain suffixes, and each of them stands for a different thing. For example, some of the TLDs are:
- .com – commercial websites,
- .edu – educational institutions,
- .net – Internet administrative websites,
- .org – non-profit organisations,
- .co – commercial websites (the same as .com),
- .au – Australia,
- .nz – New Zealand, or
- .co.uk – a commercial website located in the UK.
To find out all major Internet domain suffixes, follow this link to a full listing.
The following slideshow Understanding Domain Structure for Beginners sums up the main points related to domain structure, hierarchy, and significance.
Great! Now you should understand the difference between all the critical terms. If not, take a look at this short video that sums it up for you quickly:
Now, we can move on.
While we explained all the parts of an URL in detail, we only mentioned the protocol part. In the following section, we’ll explain a little bit more about it.
HTTP vs HTTPS vs FTP
You’ve probably noticed the same initial part of each web address in your address bar, haven’t you? It’s also important and usually automatically added by most browsers so that you don’t have to worry about typing it.
Or you have no idea what we’re talking about? Well, you should care and here’s why and what it really means.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) refers to allowing communication between different systems. In most cases, it is used for transferring data from a web server to a browser in order to view web pages.
If you want to go into more technical details about this, you can check the following presentation.
What could be a problem with this is that it is NOT encrypted which means it is NOT safe enough. In other words, anyone can see your passwords, credit card details, and the like. Obviously, this is a big issue for eCommerce stores.
Take a look at Wicker eCommerce store that uses the HTTP. You can see it at the beginning of the URL.
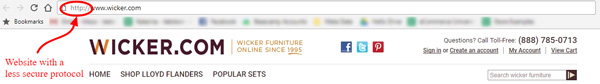
However, in most cases, the characters http:// won’t be presented and there will be a notification sign there, warning about the website security levels. Like this:

Still, the problem can be solved by using a secure version named HTTPS. Here ’s’ stands for ‘secure’.
You may ask yourself now – Why is this relevant to me?
Here’s a video explaining what HTTPS is, how it differs from HTTP, and why it matters.
Oh, now it makes much more sense, right?
You see? It is imperative in cases you have to leave any confidential data on a website. For example, when doing any business related to eCommerce, in most of the cases, you leave your credit card details on the web.
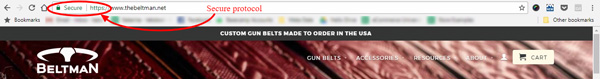
So, now when you know all this, before leaving any personal or confidential data just take a look at the top left corner of the address bar. If you see that small ‘https’, there’s a security certificate running on that website, which guarantees that your delicate private data will be encrypted and protected.
We can see this on The Beltman website:
Another transfer protocol completely different from the previous ones is FTP, which stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is also used for transferring files, but it is older than HTTP and HTTPS.
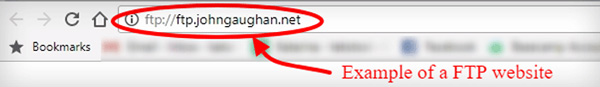
Here are some basics for you to realise what it is and how it works.
OK. Now you’re familiar with the basic ways and channels information travel through the Internet, it’s time to show you HOW exactly that process works. Ready?
Packets of Information
Imagine it’s your first day working as a chef in a kitchen of an expensive, stylish restaurant. Now, can you imagine performing your daily duties not knowing how to use the knives and the pots? Certainly not!
It’s exactly the same when you want to start working online without the basic comprehensive knowledge of how data move around the Internet. Yes, it’s true that it runs through cables and Wi-Fi. But HOW?
What it really does is – it actually moves through in flashes of light and packets of information.
Even the file you are reading now (this lesson) is delivered to you in very small packets of information. It will be a kind of chopped up, like a jigsaw puzzle, transferred in those pieces to your computer, where it will get and reassembled to its original state. Amazing!
Watch this video to see how data is transferred on the Internet.
Data principally travel through the Internet in noughts and ones, that is to say, in binary code. But why do computers use binary? Here’s an explanation of how binary code works.
That’s fine but how can a computer ‘read’ and ‘write’ text using this binary system? Follow the link, and you’ll find out how computers convert text into binary 0s and 1s. Amazing!
Another important fact for you to know is that HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a fundamental element of every webpage and you should be familiar with its basics since you want to create content for the web. Follow this link to learn all you need to know about working with HTML.
Now you know a lot more about the Internet than at the beginning of our lesson, right? But we won’t stop yet!
Here’s another useful point you have to understand, and we’re about to explain to you what it is, how to use it, and why you may find it helpful.
Archive.org
Did you know that you can access and search a website which is no longer directly available on the World Wide Web? Fascinating, isn’t it?
Yes, you can check what more than 298 billion web pages looked like at their very beginnings thanks to the amazing Internet Archive or Wayback Machine.
It is like a shadow of the Internet, its history. So, if a website is reasonably popular and not buried at the bottom of the Internet, you’ll be able to find it here.
You wonder why you would want to use it? Well, because looking at the history of something gives you more detailed and in depth information, which is why the history is just as important as the present.
Here are a couple of reasons why Archive.org is so useful to you as an online worker to-be.
- It shows you how the website used to look like, which is very useful if you accidentally delete anything (a piece of information or a whole page). Archive.org enables you to retrieve images, text, or any other information from a website you might have deleted accidentally.
- Then, if you’d like to work for an online store you’ve never heard about before, it would be wise to check the history of its website, right? This way, you’d find out e.g. whether the store even existed a few years ago, whether the business is growing (was it bigger or smaller), etc. so that you can decide if there’s a future prospect for you within the company.
Got it? You’ll come up with more reasons for sure once you think it through and start working in eCommerce.
Now, let’s check how it works. We’ll take an online shop to illustrate the process, for instance, Haigh’s Chocolates. If you follow this link, you’ll see how it looks today in 2017:
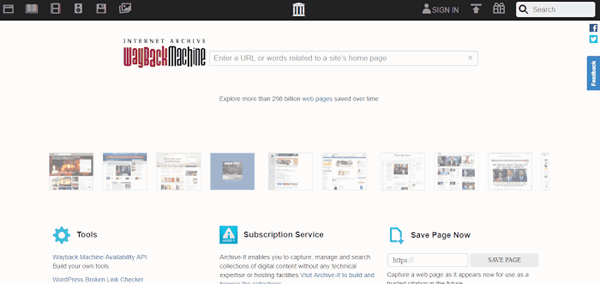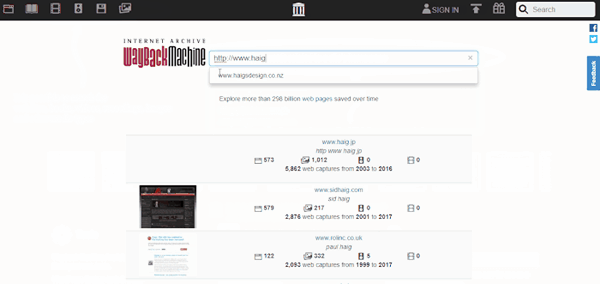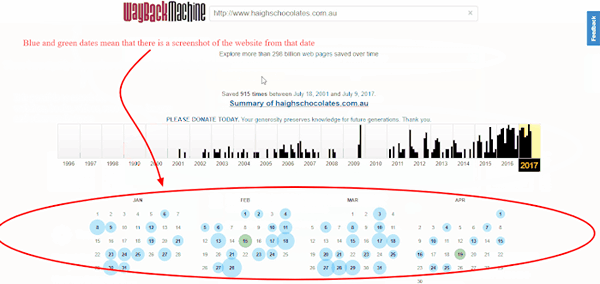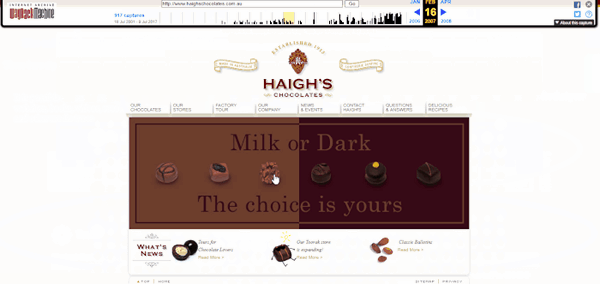
However, if you’d like to know what it used to look like e.g. ten years ago, you’ll have to search it in the Internet Archive. This is the same website, but from 2007.

Wonder how we know? Here is the video explaining how to use these amazing tools to search for the previous versions of websites.
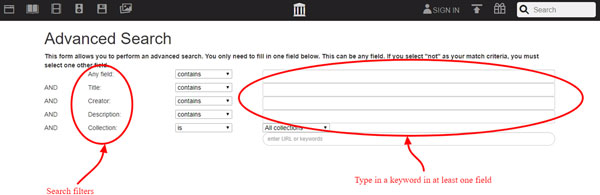
Furthermore, you can perform an Advanced Search within Archive.org! Follow the link to see the search parameters offered, search terms and operators explained, as well as some example queries.
These are only some basic features of the tool which is key to earning your living from the comfort of your home. It’s your bread and butter if you want to work within the competitive eCommerce industry, and that’s why you should care to know more.
If you are keen to keep learning, follow the links to the sources suggested in the Further reading subsection below and do your own research on the topic.
Further Reading
Here are some additional reading resources that can provide you with more in-depth knowledge on certain topics found in this lecture.
Short History of the Internet
- Business Insider: What Is the Internet and How the Internet Works
- Computer Hope: Internet
- Explain That Stuff: Internet
- Internet Live Stats: Total Number of Websites
- History of Things: History of the Internet
- Mines Press: The World Wide Web of the Late ’90s
- Invest in Tech: History of the Internet
Web address and its elements
- Doepud: Anatomy of a URL
- Moz: What is a URL?
- Stoogles: URL optimization
- Moz: What is a Domain?
- All SEO Stuff: URL vs Domain
- Practical Ecommerce: The Best URLs Contain Keywords
- Life Wire: What Is an IP Address?
- BigCommerce Support: Domain Name Basics
- iMarc: Recommended URL structures for global websites
- Moz: Study: How Searchers Perceive Country Code Top-Level Domains
- Practical Ecommerce: Creating the Perfect URL, or Not
- Rank Watch: A quick go through for URL optimization tactics
Packets of information
- The Geek Stuff: Journey of a Packet
- Tech Target: Difference between circuit-switching and packet-switching in examples
- How Stuff Works: Bytes
- How Stuff Works: Router
In Summary
Now we’ve covered the basics of how the Internet works, don’t you have a slightly better understanding of it than you did at the beginning of the lesson?
It’s easy to be deceived and start thinking you know everything about the Internet just because it’s everywhere around you. It has become a multifunctional tool, widely used for communication, retail, research, entertainment and numerous other purposes.
However, you’d want to approach it seriously since it will soon become your primary tool for work, right?
So, let’s sum up the main learnings!
The Internet has undergone many drastic changes in the recent times, and it evolved from text only information at its early days all the way through to current media-rich web pages (images, videos). You must stay tuned in since you want to work online.
In addition to keeping up with its constant changes, you must be familiar with the basic terminology to be able to communicate with other online workers worldwide.
Thus, you’ve learnt the meaning and function of the core networking terms and acronyms such as URLs, domains, subdomains, domain suffixes or TLDs, IP addresses, HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, HTML, packets of information, and Archive.
Last, but not least, you are bound to lifelong learning with the Internet used for business, and its rapid changes. Fortunately, it’s fun and rewarding!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. The ‘S’ in HTTPS stands for:
a. System
b. Standard
c. Steady
d. Secure
2. It doesn’t make a difference whether you use HTTP or HTTPs while shopping on the Internet
a. Yes. It’s all the same so it doesn’t matter which one you use
b. No. Preferably HTTPS should be used because that way your sensitive data will be encrypted and protected, which is not the case with HTTP
3. How do data basically move around the Internet?
a. In files
b. In folders
c. In envelopes
d. In packets
4. TLD is the same as domain suffix
a. True
b. False
5. In the example http://www.alsco.com.au, root domain is:
a. alsco.com.au
b. www.alsco.com.au
c. Neither of the above
6. It’s possible to see the history of changes to a website and to retrieve the information one accidentally deleted thanks to the:
a. Internet Archive
b. Wayback Machine
c. Both of the above because it’s the same
